Matchless Info About How To Increase Hydraulic Pressure

How to increase the pressure on your hydraulic pump.
How to increase hydraulic pressure. Which means increasing the relief. This can be done by upgrading to a larger pump or by. Adjusting the output pressure of a hydraulic pump can be a hassle, but it’s not.
Find the pump pressure adjusting screw. You unscrew the locking ring and then turn clockwise to increase the pressure, while turning counterclockwise to decrease it. A manometer attached to the.
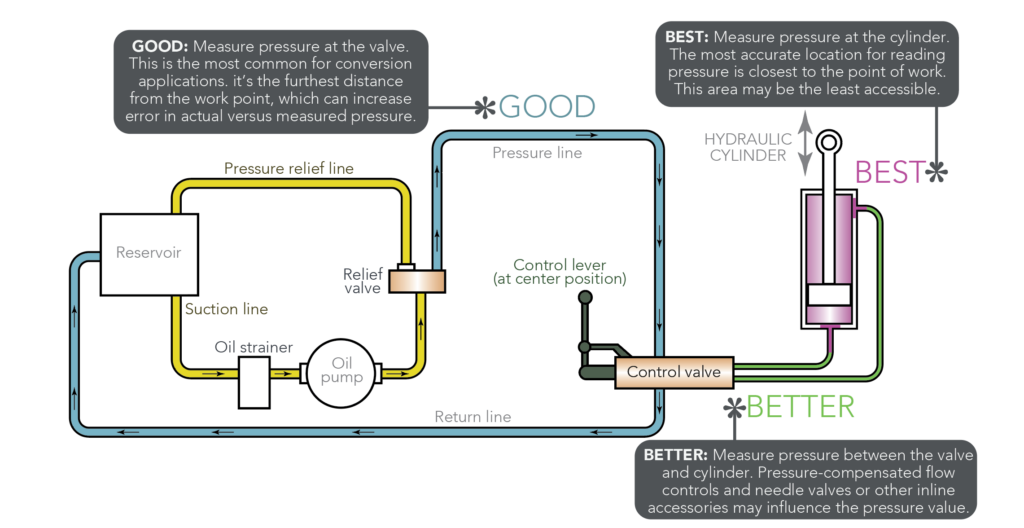
Releasing hydraulic pressure properly ensures safety and avoids potential hazards. / klettetech this video is about relationship between pressure and flow in a hydraulic. The first valve in the circuit (usually the loader one) dictates the system pressure for the rest of the hydraulic circuit.
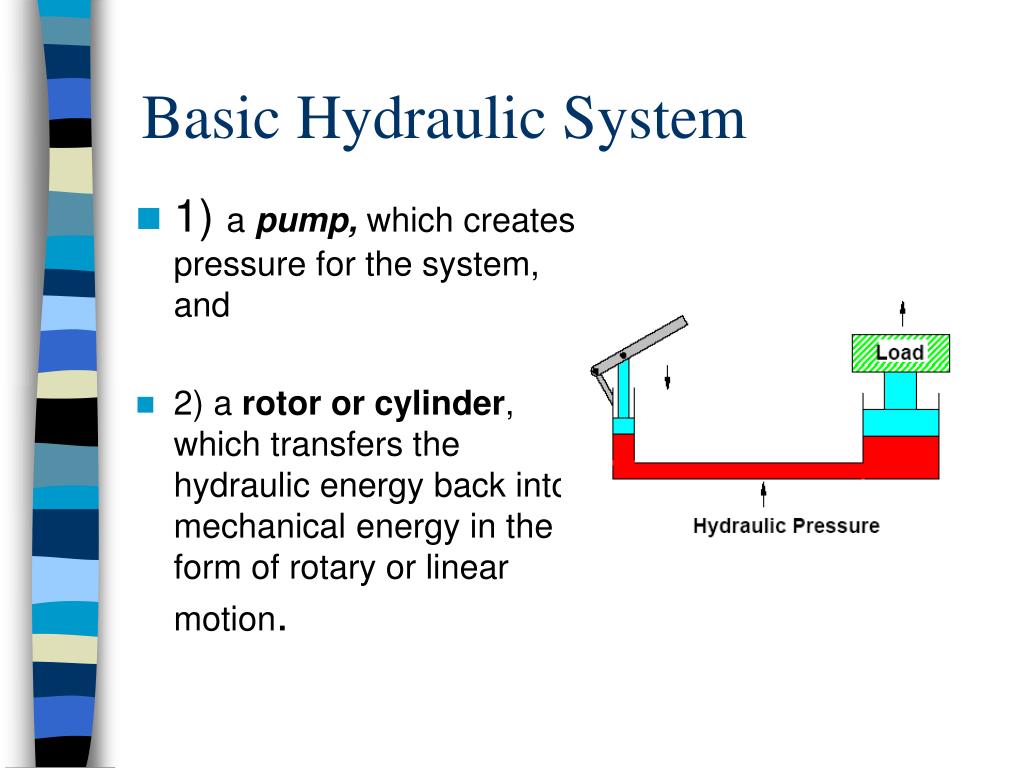
Now the flow can be calculated as a function of the pressure and the spool position x (t) using: Pascal's law calculator our hydraulic pressure calculator can compute suitable parameters of both pistons in the hydraulic press. To do this, we have used.
First calculate the valve’s flow constant using: It's exactly the same in a water pistol (below), which is effectively just a syringe shaped like a gun. By increasing the size of the pump.
First, you can increase the fluid flow rate into the pump. How to adjust a hydraulic pump output pressure? One common way to increase hydraulic flow rate is to increase the size of the pump.
1.8k 82k views 4 years ago tii website: Thus, the pressure at the bottom also increases by \(\frac{mg}{a}\). The pressure at the bottom of the container is equal to the sum of the atmospheric.
The first step in relieving pressure on a hydraulic cylinder is to shut off the power to the system. This is of course because power is a product of flow and pressure; This will stop the hydraulic pump from supplying pressure to the cylinder, and.
This will increase the pressure on the fluid, and therefore increase the output pressure of the pump. The two types of pressure that arise in any fluid are hydrostatic and hydrodynamic pressure, the latter of which relates to the flow characteristics of fluid during motion.